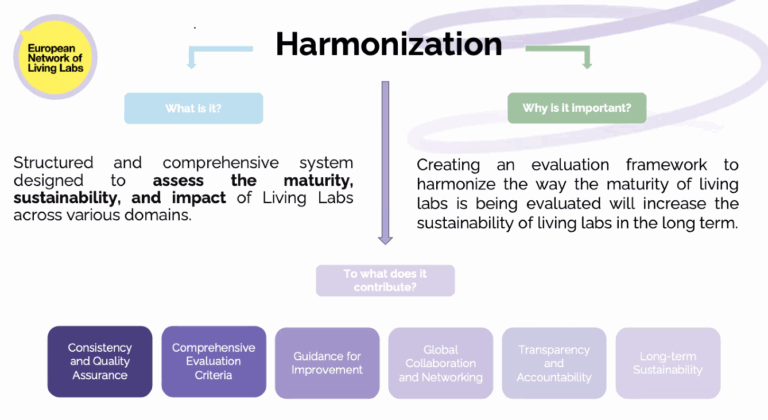
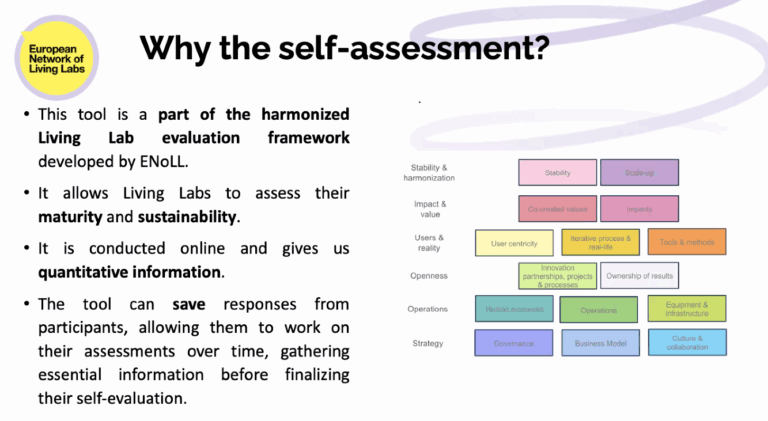
The final session of the EVOLVE2CARE Training Series for HealthTech Innovators and Researchers was held on 19 September 2025, bringing the six-part journey to a close with a focus on how to measure meaningful outcomes and scale innovation with purpose. The session, titled “Measuring Impact & Scaling Pilots — Driving Evidence-Based Growth in Living Labs,” was led by Despoina Petsani, Project Manager at ThessAHALL – Thessaloniki Action for HeAlth & Wellbeing Living Lab.
Drawing from practical experience and Living Lab methodology, the session guided participants through the mindset and tools needed to move from small-scale pilot projects to real, system-level change.
From activities to outcomes
Despoina Petsani opened with a key challenge in innovation evaluation: many projects focus on reporting what they did (outputs), rather than what they achieved (outcomes). For example, counting users reached is not the same as understanding whether user behavior or well-being improved. To build real impact, innovators must start with clear goals and plan for measurable change from the beginning.
Planning for impact from day one
Participants were encouraged to define 2–3 priority outcomes before launching a pilot. These should be tied to the needs of users and stakeholders. The use of SMART indicators—Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound—was recommended to track progress clearly and objectively.
How to evaluate a pilot
Effective evaluation goes beyond proving that something worked. It explores how, why, and for whom it worked. Despoina presented a step-by-step evaluation framework that includes:
Defining pilot objectives (What are you trying to learn or prove?)
Set evaluation questions (e.g., Does this tool improve patient engagement in rural clinics?
Set evaluation questions (Who are your users? Where and how long will the pilot run?)
Set evaluation questions (Understand the “before” to measure the “after”)
Ethics and Privacy (Data protection, informed consent – especially in health and education sectors)
A mixed-methods approach was strongly recommended, blending quantitative and qualitative tools to provide both scale and depth.
Scaling pilots responsibly
Scaling isn’t simply about growing bigger—it’s about expanding what works, in ways that fit new contexts. Before scaling, a solution should show strong user feedback, positive outcomes, operational readiness, and a clear value proposition.
Three paths to scale were introduced:
- Replication – Apply the same model in a similar setting – High control, but limited adaptability
- Adaptation – Tailor to different user needs/settings – Maintain core principles, flex where needed
- Dissemination – Spread knowledge, frameworks, and tools – Enable others to replicate/adapt independently
- The instructor also emphasized the importance of partnerships, technology infrastructure, business model and policy and systems alignment.
Final reflections
The session closed with a strong message: evidence is essential for impact. It builds trust, informs decisions, and enables scale. Living Labs and innovators must embed evaluation early and treat it not just as a reporting tool, but as a driver of learning and growth.